In modern industry, various machines have increasingly demanded precision, speed, noise and compactness of gears, especially in the aviation field, which requires gear transmission with high strength, low noise and high power density. Therefore, how to greatly improve the bearing capacity and meshing quality of the gear transmission and extend the service life of the gear is an important research topic. The application of new technologies, the exploration of new tooth shapes and their new processing methods is an important way to tap the bearing capacity of the gears and improve the transmission performance.
Due to its superiority in design, processing, inspection and assembly, the most widely used involute cylindrical gears have gradually formed a complete set of mature processing methods and equipment, and have long dominated. However, due to its inherent convex and convex contact mode, the integrated radius of curvature of the tooth profile is strictly limited by the center distance, and affects the increase of the contact strength of the tooth surface and the formation of the dynamic pressure oil film. The unevenness of the tooth surface sliding coefficient is large, resulting in gear teeth. Wear and life is reduced. In order to supplement the characteristics of insufficient strength of involute gears, scholars have proposed various types of cylindrical gear transmission forms, such as arc gears, parabolic gears, arc-toothed cylindrical gears, micro-segment gears, misaligned cylindrical gears, etc. Wait.
New gear technology
Cylindrical gear transmissions using convex-concave meshing modes mainly include arc gear transmission, parabolic gear transmission, and arc-toothed cylindrical gear transmission. The former two use the convex-concave meshing between the tooth profiles, while the latter uses the convex-concave meshing in the tooth direction direction, and the effects are different. In addition, there are new types of convex and concave mesh gears such as micro-segment gears and point-line meshing gears, which are still in the preliminary research stage.
(1) Parabolic gear
As early as the early 1980s, Professor Wen Zhifu proposed the concept of line contact parabolic gear (see Figure 1) and applied for the Chinese patent (CN86100544) [2]. The purpose of the invention was to greatly improve the cylindrical gear. Carrying capacity.

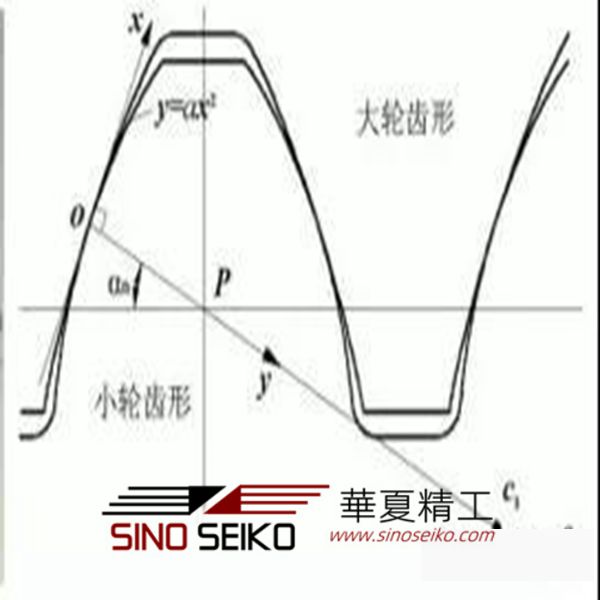
Figure 1 Parabolic gear and tooth profile
In the later published monograph [3], three basic tooth shapes of parabolic gears were proposed, named PWX-I, PWX-II, and PWX-III. The PWX-I type is similar to a double-arc gear, which is a convex tooth outside the pitch line of the gear, and a concave tooth inside the pitch line. A pair of parabolic gears can be processed with a hob; and PWX-II and PWX-III They are the basic tooth profiles of the hobs that cut the pinion and the large gear with only one meshing zone, respectively, similar to the two hobs used to machine the pinion and bull gear of a single arc gear pair. In terms of processing, the method of using a hob to cut a parabolic gear is studied. The same hobbing machine of the involute gear is used to introduce the design and manufacturing measurement method of the hob.
In terms of application, in 1981, the modulating parabolic gear of Modulo 3 was used to replace the carburizing and hardening involute gear of the 40 marine gearbox. It was used on the inland tugboat of Shazhou Shipping Company. After 6 years of operation, the inspection was not carried out. damage. In 1983, the modified nitride parabolic gear was used in the MB170 marine gearbox, the hardness was HRC50-55, the modulus was 3, the transmission power was 105 hp, the single-stage transmission ratio was 5.06, and the same type of carburizing and hardening involute involute The gearbox is docked. As the speed-increasing box of the involute gearbox, under the full-speed and full-load conditions, the box is inspected after 500 hours of endurance test, the tooth surface is in good contact, no spot is etched, and the noise is normal. Tests have shown that the nitriding parabolic gear after hobbing is equivalent to the high load carrying capacity of the carburized and hardened involute gear of the same technical parameters. After being loaded by the Wuxian Shipping Company and the Sand Shipping Company of Jiangsu Province, the application effect is good.
In addition, the boiler speed control box designed with parabolic gears is half the weight of the ZKL boiler speed control box with the original involute gear. In the direct-acting mill, the parabolic gear is used as the transmission box, and the obvious effect of eliminating the two-way involute gear is also obtained. The parabolic gear is used as the transmission of the flexible tube pump, and only one level is used. The parabolic gear reaches the transmission ratio of 11.33, which satisfies the transmission demand. Compared with the involute gear, the former has a manufacturing cost of only half of the latter. It is used for ordinary gear reducer, and its load capacity (power) can reach 220%~270% of similar involute gear reducers [3].
The basic characteristics of the parabolic gear, the design calculation method, the manufacturing process, the accuracy test, etc. are introduced in detail in [3], and the sliding rate of the tooth profile, the machining interference, the relative principal curvature, the thickness of the root limit working point and the transmission can be Several aspects such as "dividing" are compared with involute gears, and the advantages of parabolic gears are analyzed. However, some of the design calculation methods, especially the strength calculation and the meshing characteristic analysis, are relatively simple. For example, the calculation of contact stress and bending stress is based on the Hertz formula and the Lewis-Hirschmann formula, so the error is Large; theoretically simply analyzed the properties of the meshing line and the contact line, without considering the influence of the mounting manufacturing error on the meshing characteristics and strength; due to the lack of computer technology at the time, there is no meshing stiffness, transmission error and modification. Analytical research was carried out; the grinding method was not discussed. The form of engagement of the line contacts makes the parabolic gear still sensitive to mounting errors. All of this makes the ability of the parabolic gear not revealed.
Although it has been seen from many test results and trial practice in some enterprises that the parabolic gear has achieved a good effect of significantly improving the load carrying capacity, with the development and standardization of single arc gears and double arc gears in the same period In general industry, the demand for high load capacity cylindrical gears has been met by arc gears. Therefore, parabolic gear has not been taken seriously for many years. With the development of new gear analysis and design techniques, the transmission performance of parabolic gears can be continuously explored. In addition, the emergence of modern CNC gear grinding machines provides the possibility of grinding teeth machining of high-precision hard-toothed parabolic gears, so parabolic gears have great application potential.
Litvin proposed a new type of point-contact parabolic gear in the literature [4, 5]. The gear transmission combines features such as convex-concave meshing and point contact, featuring low stress, low error sensitivity and ability to grind teeth. The paired gears adopt different parabolic parameters, and the preset parabolic transmission error is obtained by crowning the teeth to reduce the vibration noise. The principle of the development of such parabolic gears is given and the strength performance of such gears and modified involute helical gears is compared by finite element analysis, indicating that the gears are in contact with the same parameters of the involute helical gears. Both strength and bending strength are high. As shown in Fig. 1, the phase-engaging tooth profile can adopt a large radius of curvature to obtain a large relative radius of curvature, which significantly reduces the contact stress. The contact can be reduced by using a large difference in curvature radius between the tooth profiles (the two tooth profiles shown in Figure 1 have c1 and c2 at the contact point O, respectively, and the distance between them can be adjusted) The sensitivity of the impression to the center-to-center error is such that the noise of the transmission is small. The point meshing parabolic gear has been compensated by the large curvature radius due to the large stress difference caused by the large curvature difference. At the same time, because the tooth shape is simple (closer to the involute gear), it can be easily used to form the grinding teeth, and the carburizing and quenching process can be applied to improve the hardness of the tooth surface. Therefore, it is suitable for high-speed heavy-duty transmission, and it is very promising to replace the aviation high-speed. Involute gear in the drive.
(2) Arc gear
The concept of circular arc gear was first proposed by American engineer Wilf Haber in 1926 [1,6,7], and then the former Soviet Union's Novikov completed the discussion of its meshing principle and strength calculation, and began to Industrially applied. Therefore it was named Wildhaber-Novikov gear, referred to as W-N gear. After decades of research, China has made great achievements in the basic theory and manufacturing process of circular gears. The basic meshing theory of the point meshing circular arc gear (normal arc) with Chinese characteristics is established; the calculation method of bearing capacity is established. Theoretical analysis and calculation of thermal elastohydrodynamic lubrication; principle and calculation of tooth end modification; accuracy test and measurement size calculation; a series of basic theories and techniques such as hob tooth design and calculation and manufacturing process, which make China's arc gear transmission technology research Walking in the forefront of the world. A number of national standards such as tooth profile, tool and strength calculation of single arc gear and double arc gear have been established. Widely used in low-speed heavy-duty industries such as metallurgy, mining, petrochemical, transportation, etc., but also in high-speed gear transmission such as steam turbines and compressors.
There are few reports on the study of arc gears abroad, mainly in the literature of Professor Litvin [8]. In [8], the tooth profile, geometry, meshing and contact of the circular arc gear are studied. The contact path of the tooth surface and the main contact direction of the instantaneous contact ellipse are determined, and the transmission error caused by the installation error is studied. "Local integration" technology. There are many discussions about arc gears in China [6-9], mainly related to tooth shape parameter design, stress analysis, load distribution, running performance and wear, hobbing scraping and other processing techniques and methods. It has played a significant role in improving the bearing capacity of circular gears and promoting the development of standardization and wide application. In terms of grinding technology, the literature [9] pointed out that the processing method of grinding the circular gear by the forming grinding wheel is not mature, and no other related reports have been found. The arc gear has very strict requirements on the deviation of the root circle. The efficiency of the radial feed of the gear grinding machine is too low, so the added value (value) of the product is too low, and the economic benefit is not high. In the general industry, there is a tendency to not grind teeth to reduce costs and improve market economic efficiency. The current national standard arc gear has the highest precision grade of 5, and the process is medium hard tooth surface modulation. The surface is nitrided after hobbing and cutting. The machining precision of carburized and quenched arc gear can only reach 6 grades. Can not meet the requirements of the aeronautical cylindrical gear transmission line speed of 160m / s or more.
In order to improve the reliability and maintainability of the helicopter main reducer, and also improve the contact strength and flexural strength of the teeth and the anti-adhesive ability, the aviation industry has done a solution to the application of the arc gear transmission to the helicopter main reducer. Related research [10], but did not report the relevant research results, mainly because the arc gear is too sensitive to the tooth profile error and installation error. In recent years, new types of transmissions such as three-arc gears and four-arc gears have emerged. These studies have made valuable efforts to continue to develop the bearing potential of arc gears.
(3) Arc-toothed cylindrical gear
The arc-toothed cylindrical gear is a new type of cylindrical gear with curved teeth (as shown in Figure 2). It has the advantages of high bending strength, no axial force and stable transmission. Since 1965, some scholars at home and abroad have carried out theoretical research and process exploration on arc-toothed cylindrical gears [11-13].

Figure 2 arc-toothed cylindrical gear
In theory, the geometric equations such as tool tooth surface, contact line, conjugate tooth surface and end face truncation, meshing surface and meshing line are studied. Geometric properties such as the root cut limit curve and the meshing limit curve and the curvature of the induced method are obtained. The research on tooth contact analysis and machining simulation was carried out. The machining of arc-toothed cylindrical gears is mostly gear-by-tooth processing using Gleason milling cutters. On this basis, Ma Zhenqun et al. [13] studied the tooth surface mismatch processing method. In recent years, research has been conducted on the use of a conventional hob to continuously cut teeth on a CNC gear hobbing machine, which significantly improves machining efficiency and reduces costs. Some of China's manufacturers have also successfully prototyped such gears and applied them to coal mining machinery, steelmaking equipment and other products, and achieved certain economic benefits.
The designer hopes to replace it with involute helical gears or herringbone gears in the future, but there are still some problems with this kind of gears. The main ones are: the design of arc-toothed cylindrical gears is complicated; the design of tooth width has limitations, and it also affects The increase of the degree of coincidence; the use of the circular broaching method makes the gear tooth width small and the degree of bending low; and the hobbing machine processing requires a 6-axis linkage CNC machining machine, so it is not easy to popularize.
in conclusion
In summary, the gear design will advance toward the advanced technology, active design method and reliability improvement to reduce the meshing impact and noise, improve the transmission performance, and improve the contact line load, tooth surface stress and root stress. The development of the shape and the shape of the shape to achieve the minimum dynamic load angle. Internationally, power transmission devices are developing along miniaturization, high speed, low noise, and high reliability. The research and development of tooth profile design must comprehensively consider these characteristics, and tap the inherent potential of special toothed gears to meet the fundamental needs of modern high-speed heavy-duty gear transmission.
The tooth profile of the high-intensity gear tends to use a form of convex-concave engagement, while the high-speed transmission requires the gear pair to be separable, low in error sensitivity, and low in transmission error. The tooth width design of the circular toothed cylindrical gear is an unsolved important problem, which limits the increase of the transmission coincidence degree and strength; the convex and concave tooth profile curvature of the circular arc gear is almost equal and the separability is poor, and neither It is allowed to use the modified radial depth of cut to optimize the transmission error; in contrast, the new point contact parabolic gear uses a very large relative radius of curvature to meet the strength and "divisibility" requirements, while Low transmission error allows for better dynamics. Therefore, in the field of high-speed heavy-duty, including the development of new high-power high-speed transmission, point-contracting parabolic gear has great development prospects.
Contact: Sino Seiko
Phone: +8613353772661
Tel: +8613353772661
Email: [email protected]
Add: Zhengzhou, Henan, China